The voltage on a car battery should be around 12.6 volts. A car battery is essential to a vehicle’s electrical system, providing the necessary power to start the engine and run various electrical devices.
Understanding the voltage of a car battery is imperative for maintaining optimal performance and preventing potential issues. The ideal voltage for a car battery is typically around 12. 6 volts when fully charged. This voltage ensures sufficient power to start the engine and effectively operate all the electrical components.
Monitoring the voltage of a car battery is crucial for identifying any potential charging or battery health problems and taking appropriate action to prevent unexpected breakdowns. We will explore the importance of maintaining proper voltage levels on a car battery and discuss ways to monitor and maintain its health effectively.
The Importance Of Proper Car Battery Voltage
The proper car battery voltage is crucial in ensuring optimal vehicle performance. The voltage on a car battery should typically be around 12. 6 to 12. 8 volts when the engine is off, and 13. 7 to 14.
7 volts when the engine is running. Maintaining the correct voltage helps to preserve the battery’s lifespan and ensures efficient electrical system operation.
Understanding Voltage And Its Significance
The voltage of a car battery refers to the electrical potential difference between its positive and negative terminals. In simple terms, it is the force that drives the flow of electrons within the battery, supplying the necessary energy to start the engine and power various electrical components of your vehicle. The voltage value indicates the strength of the battery and its ability to deliver power to the electrical system efficiently.
A standard car battery typically operates at around 12 volts. This value is essential because it ensures the battery can provide enough electrical energy to start the engine reliably. Moreover, it ensures that the battery can sustain the power demands of the headlights, air conditioning system, radio, and other electrical accessories while the engine runs.
A higher voltage may harm your vehicle’s electrical system, potentially damaging sensitive components like the alternator, computer systems, and fuses. On the other hand, a low voltage can lead to slow engine cranking, poor performance, and even failure to start in extreme cases.
Consequences Of Incorrect Voltage Levels
When the voltage of a car battery deviates from the optimal range, several consequences can occur:
- Poor engine starting: A weak or low-voltage battery may struggle to provide the necessary power to start the engine, resulting in slow cranking or failure to start altogether.
- Dim headlights and electrical issues: Insufficient voltage can cause dim or flickering headlights, as well as malfunctions in electrical components such as the radio, power windows, and dashboard lights.
- Overcharging: Excessive voltage can lead to overcharging, damaging the battery and reducing its lifespan. This can also affect the performance of other electrical components.
- Undercharging: If the battery voltage remains consistently low, it may not receive enough charge, leading to a constant state of undercharging. This can result in premature battery failure.
Ensuring that the voltage of your car battery is within the recommended range is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and preventing potential damage. Regularly monitoring your battery’s voltage can help you identify any issues early on and take the necessary steps to rectify them.

Credit: www.amazon.com
Factors Affecting Car Battery Voltage
When it comes to maintaining the performance of your car battery, understanding the factors that affect its voltage is crucial. The voltage of a car battery directly influences its ability to start the engine and power the various electrical components of the vehicle.
By considering key factors such as temperature and internal resistance, you can ensure optimum battery voltage and prolong the lifespan of your car battery.
Temperature
The temperature surrounding your car battery plays a significant role in determining its voltage. Extreme temperatures, whether hot or cold, can impact the efficiency and overall voltage of the battery. Cold weather, in particular, can significantly decrease voltage output, making it more challenging for the battery to function correctly.
On the other hand, excessive heat can accelerate the rate of internal chemical reactions in the battery, leading to increased self-discharge and potential damage to the internal components. It is crucial to note that different battery types have varying temperature thresholds, and understanding these limits is essential for maintaining optimal battery performance.
Internal Resistance
Another critical factor influencing car battery voltage is its internal resistance. Internal resistance refers to the resistance of the battery’s internal components as electricity flows through them. Any increase in internal resistance can lead to voltage drops and reduced battery performance.
Multiple factors contribute to internal resistance, including battery age, chemistry, and environmental conditions. As a battery ages, internal components can deteriorate, causing an increase in resistance. Exposure to extreme temperatures, humidity, and vibration can also contribute to internal resistance and affect battery voltage.
It is worth mentioning that regular battery maintenance, such as cleaning terminals and ensuring proper electrical connections, can help minimize internal resistance and maintain optimum voltage levels.
Measuring And Maintaining Voltage Levels
Measuring and maintaining the voltage levels of your car battery is crucial to ensure its optimal performance and longevity. By regularly monitoring the voltage and implementing preventive maintenance, you can prevent unexpected breakdowns and extend the lifespan of your vehicle’s battery. Below are essential tips on measuring the voltage and maintaining it at the recommended levels.
Using A Multimeter
One of the most effective ways to measure the voltage of a car battery is by using a multimeter. Follow these steps to measure the voltage with a multimeter:
- Locate the battery terminals and ensure the vehicle is turned off.
- Set the multimeter to DC voltage mode and adjust the range to at least 12 volts.
- Connect the positive (red) probe to the positive terminal of the battery and the negative (black) probe to the negative terminal.
- Read the voltage displayed on the multimeter. A healthy car battery should read between 12.6 and 12.8 volts.
Preventive Maintenance Tips
In addition to measuring the voltage, several preventive maintenance tips can help maintain the optimal voltage levels of your car battery:
- Regularly clean the battery terminals to prevent corrosion and ensure a secure connection.
- Check the electrolyte levels in non-sealed batteries and top them up with distilled water as needed.
- Tighten any loose clamps or connections to prevent voltage drop and electrical issues.
- Consider using a battery maintainer or trickle charger if the vehicle is not used frequently to prevent the battery from draining.
Optimal Voltage For Different Car Battery Types
When it comes to car batteries, understanding the optimal voltage for each battery type is crucial for ensuring proper performance and longevity.
Different car battery types have different optimal voltage ranges, which must be maintained to function optimally. This article will explore the optimal voltage for two popular car battery types: lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries.
Lead-acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries are the most commonly used type of car batteries. These batteries store and deliver electrical energy using a chemical reaction involving lead plates and sulfuric acid.
The optimal voltage range for lead-acid batteries is typically between 12.4 to 12.7 volts. This voltage range ensures the battery is adequately charged and can deliver power consistently to start the car and operate electrical components.
It is important to note that exceeding the higher end of the optimal voltage range can lead to overcharging the battery, which may cause damage and reduce its lifespan. On the other hand, dropping below the lower end of the range indicates an undercharged battery, which may result in starting difficulties or insufficient power supply to the vehicle’s electrical system.
Lithium-ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries have gained popularity recently due to their higher energy density and lighter weight than lead-acid batteries. The optimal voltage range for lithium-ion batteries used in car applications is typically between 3.0 to 4.2 volts per cell. Most automotive lithium-ion batteries consist of multiple cells connected in series, which results in a nominal voltage of 12 volts.
Like lead-acid batteries, avoiding overcharging and undercharging lithium-ion batteries is essential. Overcharging can lead to reduced battery life and even thermal runaway, while undercharging can result in decreased capacity and potential damage to the battery. Therefore, it is essential to use a properly designed battery management system (BMS) to maintain the voltage within the recommended range.
In conclusion, understanding the optimal voltage for different car battery types is vital for maintaining their performance and longevity. Lead-acid batteries have an optimal voltage range of 12.4 to 12.7 volts, while lithium-ion batteries typically operate within the range of 3.0 to 4.2 volts per cell.
By ensuring that the voltage remains within these ranges, car owners can maximize the efficiency and lifespan of their batteries, leading to a reliable and hassle-free driving experience.
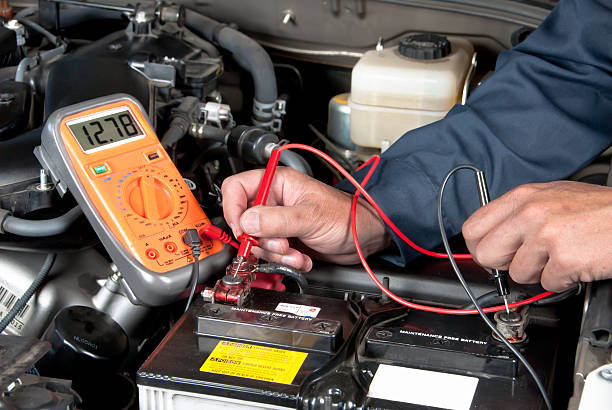

Troubleshooting Voltage Issues
When it comes to the voltage of a car battery, it’s essential to keep an eye on it and understand what the ideal range should be. Voltage issues can significantly impact the performance and lifespan of your car battery, so it’s crucial to be aware of the symptoms of undercharging and overcharging. By recognizing these symptoms, you can troubleshoot voltage issues and take appropriate action to ensure your battery functions optimally. Let’s delve into the telltale signs of undercharging and overcharging and what to do when encountering them.
Symptoms Of Undercharging
If your car battery is undercharged, it is not receiving sufficient power to maintain its optimal voltage level. This can result from various factors, such as a faulty alternator, loose or corroded connections, or a malfunctioning voltage regulator. Here are the common symptoms to look out for:
- Dim or flickering headlights: When your headlights appear dim or flicker while driving, it could indicate an undercharged battery.
- Slow engine cranking: If your engine takes longer than usual to start or cranks slowly, it may be a sign that your battery is not getting enough charge.
- Electrical issues: You may experience issues with your car’s electrical components, such as a weak sound system, malfunctioning power windows, or unresponsive dashboard lights.
- Frequent jump-starts: If your battery frequently requires jump-starts, it could indicate underlying undercharging issues.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s essential to have your battery and charging system inspected by a professional. They can determine the root cause of the undercharging issue and recommend the necessary repairs or replacements to restore proper voltage levels.
Symptoms Of Overcharging
On the other hand, when your car battery is overcharged, it receives too much voltage, which can lead to accelerated wear and potential damage. Overcharging can result from a faulty voltage regulator, incorrect battery charger settings, or a problem with the alternator. Here are the signs to watch for:
- Swollen battery case: If your battery’s case appears bloated or swollen, it may clearly indicate overcharging.
- Strong sulfur smell: A strong smell of sulfur or rotten eggs from the battery can indicate overcharging.
- Excessive corrosion: Overcharging can cause increased corrosion around the battery terminals.
- Boiling battery: When it starts overheating and releases boiling gases, it’s a red flag for overcharging.
If you notice any of these symptoms, addressing the overcharging issue promptly is essential. Overcharging can damage your battery and other electrical components in your vehicle. Consult with a professional to diagnose the cause of the overcharging and ensure proper adjustments are made to prevent further damage.

Credit: www.optimabatteries.com
When to replace car battery voltage
The decision to replace a car battery is typically based on its voltage, overall condition, and performance. Here are some general guidelines regarding when to consider replacing a car battery based on voltage:
- Voltage Measurement:
- A fully charged 12-volt lead-acid car battery should measure around 12.6 to 12.8 volts. When the battery voltage drops below 12.4 volts, it is considered partially discharged. If the voltage falls significantly lower, it may indicate a deeper discharge or a problem with the battery.
- Testing Under Load:
- Testing the battery voltage while the vehicle starts (cranking) can provide additional information about its health. A healthy battery should maintain a voltage above 9.6 volts during cranking. If the voltage drops significantly below this level, it may suggest a weak or failing battery.
- Age of the Battery:
- Car batteries typically have a lifespan of 3 to 5 years. Suppose your battery is reaching the end of its lifespan. In that case, even if it still holds a charge, it may be prudent to consider a replacement, mainly if you rely on your vehicle for essential transportation.
- Performance Issues:
- If you experience difficulty starting your vehicle, especially in cold weather, or if you notice a slow crank, it could be a sign that the battery is weakening.
- Charging Issues:
- If the battery consistently fails to hold a charge even after being fully recharged, it may be a sign of internal damage or wear, and replacement may be necessary.
- Visual Inspection:
- Inspect the battery for signs of physical damage, leaks, or swelling. If you notice any of these issues, it indicates that the battery should be replaced.
While voltage is essential, it’s crucial to consider other aspects of battery health and performance. If you’re unsure about the condition of your car battery, you can have it tested at an auto parts store, dealership, or by a professional mechanic. Some places offer free battery testing services.
Remember that these guidelines are general, and individual cases may vary. Regular battery maintenance, such as cleaning terminals, ensuring proper charging, and monitoring overall battery health, can contribute to a longer and more reliable battery life.
Normal battery voltage when car is running
When a car is running, the battery voltage should typically be higher than when the car is turned off. The alternator is responsible for charging the battery and providing electrical power to the vehicle’s systems while the engine runs. Here are some general guidelines for average battery voltage when the car is running:
- Charging Voltage:
- When the engine is running, and the alternator functions correctly, the charging voltage should be 13.5 to 14.7 volts for a 12-volt system. This voltage range ensures that the alternator provides sufficient power to charge the battery and supply electricity to the vehicle’s electrical systems.
- Steady Voltage:
- The voltage should remain relatively steady within the specified range as long as the alternator operates correctly. Slight fluctuations may occur based on electrical load and engine speed but should not deviate significantly from the standard charging voltage range.
- Voltage Drop After Starting:
- Right after starting the engine, the voltage may temporarily drop due to the high current draw during cranking. However, the voltage should reach the normal range once the engine runs and the alternator is actively charging.
- Battery Health:
- If the battery is in good condition, it will accept the charge from the alternator, and the voltage will stabilize within the specified range. A well-maintained battery should not have a significant impact on the charging voltage.
If you have concerns about the battery or charging system, you can use a multimeter to measure the voltage at the battery terminals while the engine is running. If the voltage is consistently below the normal range, it may indicate a potential issue with the alternator, voltage regulator, or other components in the charging system.
These are general guidelines, and specific vehicle models may have slight variations. Suppose you’re unsure or suspect a problem with the charging system. In that case, it’s advisable to consult the vehicle’s manual or seek the assistance of a qualified mechanic for further diagnosis and testing.

What car battery voltage is too low
A car battery voltage that is too low can indicate a discharged or weak battery, which may lead to difficulties starting the vehicle or operating electrical components. Here are some general guidelines for car battery voltage levels:
- Fully Charged Battery:
- A fully charged 12-volt lead-acid car battery should measure around 12.6 to 12.8 volts. This voltage is considered optimal for a fully charged battery.
- Partially Discharged Battery:
- A battery voltage reading between 12.4 and 12.6 volts suggests a partially discharged state. While the battery is not fully charged, it still has a reasonable amount of energy.
- Low Battery Voltage:
- If the battery voltage drops below 12.4 volts, it is considered low, and it may indicate that the battery needs to be charged. A voltage of 12.2 volts or lower is generally considered critically low.
- Engine Starting Voltage:
- During cranking (when starting the engine), a healthy battery should maintain a voltage above 9.6 volts. If the voltage drops significantly below this level, it may indicate a weak or failing battery.
If you encounter a situation where the battery voltage is consistently low, here are some potential reasons and actions to consider:
- Battery Age: If the battery is old, it may be reaching the end of its lifespan and may not hold a charge as effectively. Consider replacing the battery.
- Charging System Issues: A malfunctioning alternator or voltage regulator may not charge the battery correctly. Have the charging system checked by a professional mechanic.
- Parasitic Draw: Certain electrical components may draw power from the battery even when the car is turned off, leading to a constant drain. A parasitic draw test can identify and address this issue.
- Faulty Battery: If the battery consistently fails to hold a charge, it may be defective and require replacement.
If you are unsure about the battery’s condition or experience ongoing issues, it is recommended to have the battery tested and the charging system inspected by a qualified mechanic. They can diagnose the problem and recommend the appropriate steps to ensure the reliable operation of your vehicle.
Frequently Asked Questions On What Should The Voltage Be On A Car Battery
What Is The Ideal Voltage For A Car Battery?
The ideal voltage for a car battery is around 12. 6 to 12. 8 volts when the engine is off and at rest. When the engine is running, the voltage should be around 13. 7 to 14. 7 volts, indicating that the alternator is correctly charging the battery.
What Happens If The Voltage On A Car Battery Is Too Low?
If the voltage on a car battery is too low, it may not have enough power to start the engine. In addition, low voltage can cause electrical components to malfunction or stop working altogether. It is important to check and maintain the voltage of your car battery regularly.
Can A Car Battery Have Too High Of A Voltage?
Yes, a car battery can have too high of a voltage. When the voltage exceeds 14. 7 volts, it can overcharge the battery, leading to overheating and potentially damaging the battery’s cells. This can shorten the battery’s lifespan and cause other electrical issues in the vehicle.
Why Is It Important To Maintain The Correct Voltage On A Car Battery?
Maintaining the correct voltage on a car battery is vital to ensure the reliable starting of the engine and the proper function of electrical components. A voltage that is too low can result in a dead battery, while a voltage that is too high can damage the battery and other electrical systems in the vehicle.
Regular maintenance can help prevent these issues.
Is 12.4 volts OK car battery?
A voltage of 12.4 volts for a car battery is considered relatively low and indicates a partially discharged state. A fully charged 12V car battery typically measures around 12.6 to 12.7 volts. If your battery consistently reads 12.4 volts or lower, it may need charging or testing to assess its health.
What voltage is too low for car battery?
A voltage below 12.2 volts is too low for a fully charged 12V car battery. If it falls below this level, the battery may need recharging or testing for potential issues.
What is a bad battery voltage?
A voltage reading below 12.2 volts is typically considered a low or potentially bad voltage for a 12V car battery.
Is 11.9 volts enough to start a car?
A voltage of 11.9 volts is relatively low for a car battery and may not provide sufficient power to start the vehicle reliably. It’s advisable to recharge the battery before attempting to start the car.
Conclusion
Understanding the voltage of your car battery is crucial for its performance. Proper voltage ensures smooth functioning of the electrical components, leading to efficient vehicle operation. Regularly monitoring and maintaining the voltage within the recommended range will help prolong the lifespan of your car battery and prevent unexpected breakdowns.

I am a technology Specialized writer and blogger based in the USA & UK. I have four years of experience in Technology, Social Media and all types of Battery’s like Solar Battery,Car Battery,Lithium Battery etc. So I work on solving these issues and give various tips on these issues.